
Article Contents
Introduction
In the very beginning let us start by understanding what the phrase ‘Psychometric Test’ means. A psychometric test is a test designed to show someone’s personality, mental ability, opinions, etc.
Human psychology has always been a subject of interest for researchers, and many scientists and researchers have tried to come up with various theories about human psychology which are colloquially referred to as ‘human nature’.
They have tried to define various frameworks to define human psychology like Six Thinking Hats, Big 5 Personalities, etc. Psychometric tests have been derived from such models and theories of human psychology.
Psychometric assessments are used for various applications and entrance tests or screening tests, for example:
- Entrance Exams for Schools during Admissions
- Hiring Process for Organizations to select suitable candidates
During this selection process, it would be advantageous for recruiters and selectors to know the nature of the person apart from the skill sets or academic credentials.
Avoid the Cost of Wrong Hiring
According to the latest studies, the cost associated with faulty hiring for middle-level jobs to managerial-level jobs can hamper the growth of the organization.
This cost may vary based on the position and post for which the employee is recruited. According to a Career Builder study, wrong hiring may cost your organization around $7000 to $10,000 for a junior level or middle level or managerial position.
If you want to avoid wrong hiring then standardizing your organization’s recruitment process with custom psychometric tests and other assessment practices can be your way forward.
How can you test human psychology?
Hundreds of psychological studies have been conducted by scientists across the world. The study of human psychology involves the study of the behavioural aspects of people.
Following are some of the factors evaluated in the psychometric tests conducted by organizations during the selection or recruitment process:
- Decision-Making Ability
- Learning New things
- Communication Skill
- Team Skills (Interpersonal Skills)
- Analytical Ability

All the above-mentioned factors are related to human psychology. It may not be possible to test the entirety of human psychology at a particular given point in time, as these skills evolve with experience, time, and learning.
But the test can surely provide useful insights in terms of the ability of the individual at a particular time.
Difference between Intelligence Quotient and Emotional Quotient
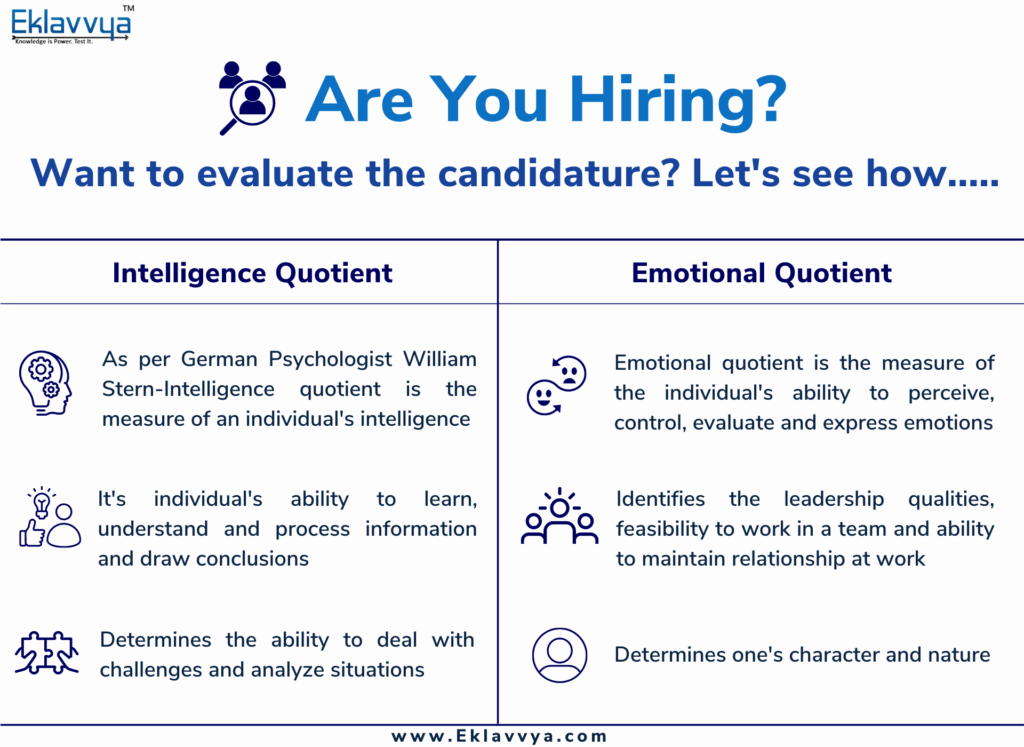
Intelligence Quotient or IQ, a term coined by German psychologist William Stern for the German term Intelligenzquotient, is the measure of an individual’s intelligence. It is calculated with the help of several standardized tests designed to evaluate human intelligence.
The IQ test assesses individuals’ ability to learn, understand and process information and draw conclusions, logical reasoning, word comprehension, mathematical skills, abstract and spatial skills, ability to filter irrelevant information, etc.
Emotional Quotient, on the other hand, is the measure of the individual’s ability to perceive, control, evaluate and express emotions. People with high EQ can manage their emotions better, use their emotions to facilitate thinking, understand emotional meanings and accurately perceive others’ emotions.
In the workplace, the Emotional Quotient or EQ is used to identify if the employee is a team player or not, their leadership abilities and abilities to build and maintain relations with colleagues and clients, how well they collaborate with others, and how often they take a new initiative.
Intelligence Quotient or IQ is used to determine the employee’s ability to deal with challenging tasks, ability to analyze situations and connect dots, research, and development, etc.
The EQ tests and IQ tests are making an emergence in the hiring or recruiting processes of many organizations. Both of these tests help organizations understand the character and the personality of the employee and often the results of these tests play an important role in the decision to hire the candidate or not.
Many organizations have made it compulsory for employees to take an EQ test before joining since the latest research has shown that there is a relationship between higher EQ and successful employees.
The EQ tests help organizations determine and identify if the candidate is a leader and/or a team player if the candidate works best alone, or if the candidate faces any social challenges. The IQ tests help organizations identify highly gifted or capable individuals, and understand the intellectual capacity of the candidate or individuals with special needs.
A few reputed EQ tests are the Mayer-Salovey-Caruso Test, a test on emotion-based problem-solving tasks, and the Daniel Goleman model Score which is based on emotional competencies.
A few reputed IQ tests are the Stanford-Binet test, the Wechsler test, and the Woodcock-Johnson Test of Cognitive Abilities.
What exactly are Psychometric Assessments?
A psychometric assessment is a test that is used to generate a basic understanding of a person’s personality and behavioral aspects. It is typically a Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ) based objective test in which the candidate needs to select one option from the available set of 4 to 5 options for each question.
The result analysis is done based on the questions and topics to come up with a mathematical scoring sheet. The score range is used to analyze individuals in terms of working style, interpersonal skills, personality (introvert, extrovert) quotient, etc.
Following are some of the benefits of psychometric tests-

1. It saves time for the evaluation of candidates.
Psychometric Assessments will give a detailed profile and analysis of the candidate. Recruiters and employers can use this analysis of the candidate’s personality traits and decide whether the candidate is the right fit for the position or not, or which different position can fit him/her the best.
2. You can get an idea of the personality and behavioral traits of the individual
By getting a detailed analysis and profile of the candidate’s various personality traits, you gain a better and deeper understanding of the candidate as an individual and as an employee.
You, with this information, can now find the right position or post for the employee and help them unlock their full potential. This will help both the employee and your organization.
Additionally, psychometric assessments can help greatly in increasing employee engagement in the workplace. Employee engagement means that employees are fully engaged in their work and are enthusiastic about it.
The HR department can use the data from the psychometric assessment to help increase employee engagement in the workplace.
3. It can save time and cost during the hiring
Recruiting new employees can be a time-consuming and costly process. If you have received numerous applications for one post, or if you recruit for multiple posts and have received multiple applications, the recruitment process can drag on for a long time and become costly.
Incorporating a psychometric assessment will help you standardize the process and make it less time-consuming and save costs.
Psychometric assessments are quick and give instantaneous results. This means that recruiters can make their minds up about hiring a particular employee with ease and quickly, without wasting time on unnecessary deliberation.
4. Online Psychometric Assessments are easy to design and are cheap and don’t take too long to attempt.
This means that your organization will benefit by saving time and money by implementing psychometric assessments in your recruiting process.
5. You can eliminate judgemental errors or mistakes of wrong hiring
This is perhaps one of the best advantages of having a psychometric assessment in your recruiting and selection process. You will understand the candidate’s nature and it will aid you in making the right decision.
By incorporating psychometric assessments, recruiters do not depend solely on interviews for recruitment. A candidate can be perfectly suitable for the job but might not be able to make a good impression in the interview due to multiple factors like nervousness, fluency in the language of the interview, and time.
The opposite can happen too, a candidate may very well make a good impression in the interview but may prove not to be very suitable for the job after they have started working with the organization.
As we discussed at the beginning of the article, hiring the wrong employee can cost your organization anywhere between US$7000 to US$10,000. By using a psychometric assessment you can avoid this mistake in hiring and save money!
The selection / Hiring Process can be standardized for the organization.
Once you have designed and customized the psychometric assessment for your organization, you don’t need to change them much or at all.
These assessments set a benchmark for the assessment of candidates and this standard remains the same for future employees, making the hiring process fair and less prone to mistakes.
Types of Psychometric Assessments
There are various types of psychometric tests or assessments available. These tests can be customized as per the requirement of the organization or entity.
1. Personality Assessment
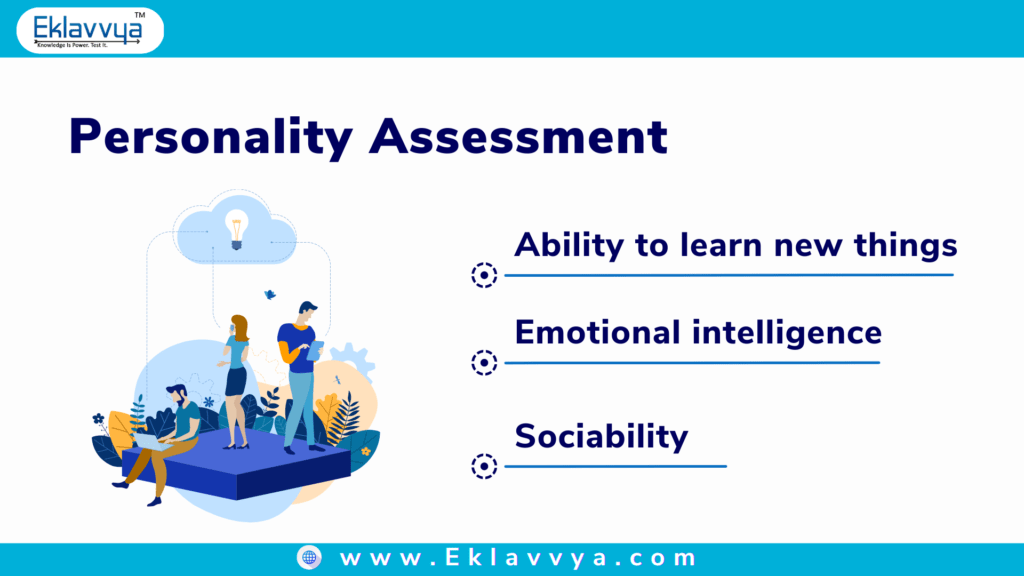
The Personality Assessment test is used during the recruitment process of the employees for the organization. It can be applied to employees across multiple levels, right from the junior level to the managerial level.
A Personality Assessment test can help to analyze the following traits:
- Ability to learn new things Emotional Intelligence Sociability
- Ability to learn new things
- Emotional Intelligence
- Sociability
2. Leadership Assessment
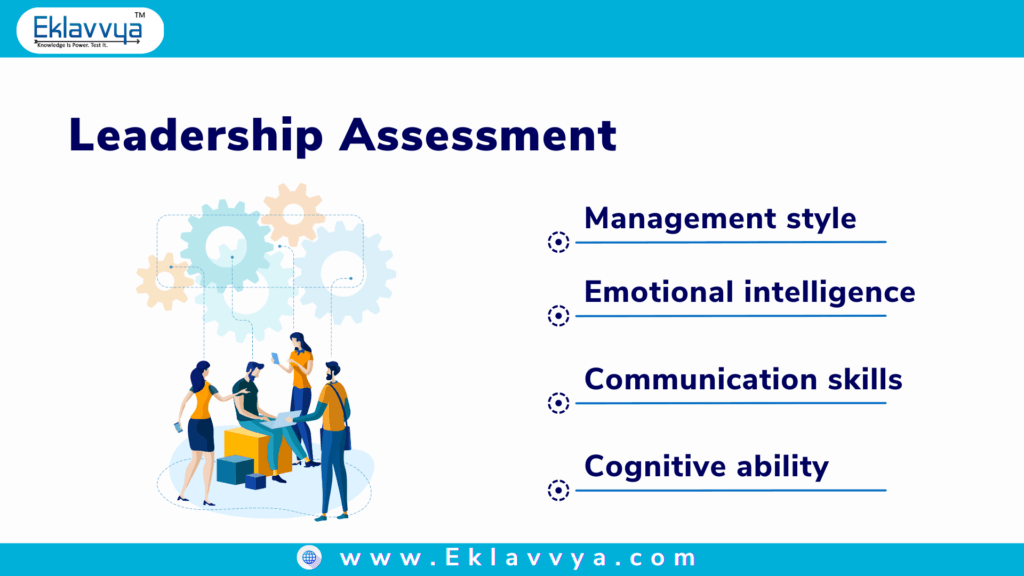
The Leadership Assessment is typically used during the hiring of a senior-level employee or filling up a managerial position in the organization. Leadership Psychometric Assessment typically is used to analyze the candidate for the following traits:
- Management Style
- Emotional Intelligence
- Communication Ability
- Cognitive Skill
Psychometric test vs Aptitude test
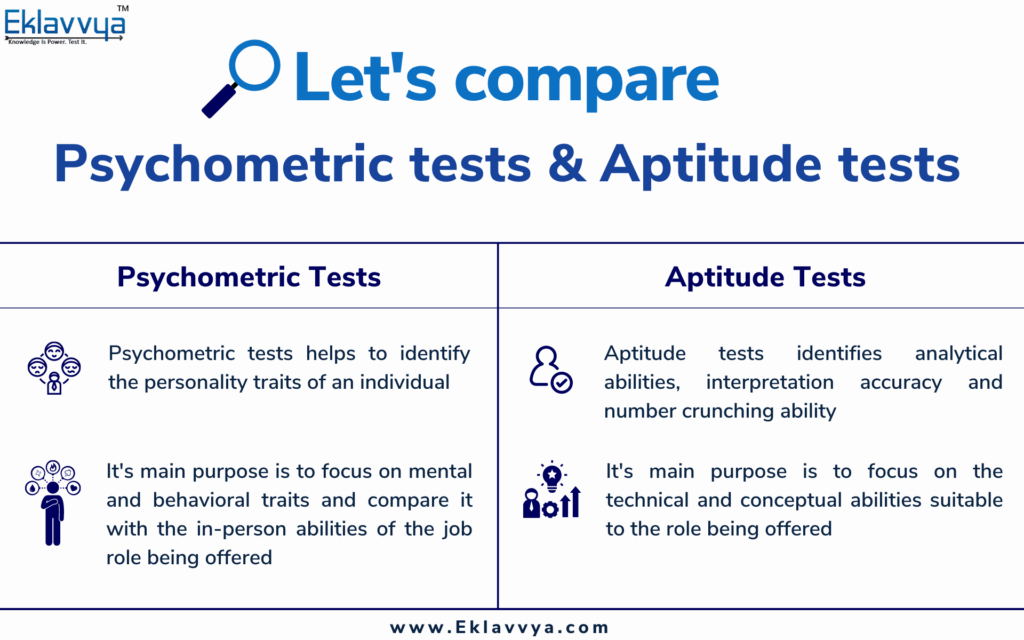
Aptitude Tests have been a popular tool to evaluate candidates for exams like Management School Entrance, selection of entry-level, freshers recruitment of employees for the organization.
An aptitude test can provide you with an insight into the ability of the individual in terms of analytical ability, ability to comprehend information, accuracy associated with interpreting information, and mathematical or number-crunching ability.
However, Aptitude Tests have limitations in terms of identifying various personality or behavioral traits of the individual.
Psychometric Tests can help rectify the shortcomings of the Aptitude Test. These tests can help you to identify the personality traits of an individual along with their liking and preferences in terms of working in a team or a client-facing role etc.
A combination of an Aptitude Test and a Psychometric Test can help you to get a detailed analysis of the abilities, skills, and personality of the individual. It can be helpful during the decision-making or the selection process.
What is involved in a psychometric test?
A psychometric test is typically an objective Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQ) test in which candidates are asked to answer questions and they need to select a response according to their preference, and nature. There are no right or wrong answers to most of the questions.
Answer options are weighted according to behavioral aspects.
Certain options may have 4 marks, other options can have 2 marks, and some of the options might have zero marks assigned. At the end of the test, candidates can get a weighted score of their performance and it can help you analyze these personality traits for the various selection processes or decision-making.
What is psychometric testing in recruitment?
Psychometric tests are being increasingly used for recruitment purposes. Understanding leadership and working in a team are key aspects that play a role in the career of anyone. These factors are especially important in the case of the recruitment of mid-level to senior-level employees.
Psychometric tests in recruitment help to identify basic traits or nature of the human being like being an introvert or an extrovert, team player, or individual performer. The outcome of the test is useful to decide the suitability of the candidate for various job roles like a team leader, research engineer, R&D, quality assurance, etc.
What type of questions are asked in a psychometric test?
The psychometric test is comprised of multiple-choice questions where you need to select one or more suitable option choices from the list of available choices shown for the particular question. Questions are framed in such a way that you are supposed to select an answer (or answers) according to your nature.
Consider the following questions:
Question: I prefer working in a silent place for doing research work.
Answer Choices:
- Some times
- Most of the time
- Neutral
- Never
Question: I am a team player who enjoys working on the team
Answer Choices:
- Some times
- Most of the time
- Neutral
- Never
User responses for the above 2 questions can be helpful to understand the nature of the person and if a person enjoys working in a team or is suitable for research-oriented work.
Is an IQ testing a psychometric test?
IQ test (Intelligent Quotient) is specifically defined to know your capability in terms of intellectuality. It helps to identify the problem-solving skills, thinking skills, puzzle-solving capability, and such abilities of an individual.
A psychometric test is designed to understand personality traits like leadership quality, teamwork capability, the nature of the person (introvert, extrovert), etc.
Psychometric tests focus on soft skills and the nature of the individual while an IQ test focuses on the intellectual capacity of the person.
Career Assessment with Psychometric Tests
Psychometric tests have been increasingly popular during the assessment and identification of preferences for students related to particular career choices. Students who are pursuing their undergraduate course or in 12th standard find it an attractive option to assess their likings, preferences, and abilities related to a particular career option.
Career Preference Assessment is designed in the form of Multiple-Choice Questions (MCQs) where students or candidates need to provide their response to the question based on their preference.
At the end of the test, the system analyzes all responses and comes up with the cumulative scores for various segments like creativity, routine task, ability to complete certain tasks, etc. The system can provide some suggestions or insights about the career likings of the candidate based on the various sectional scores.
The key to getting accurate results or analysis from such a test is to provide your honest opinions and responses to the questions. Honest responses can uncover a lot of strong and weak areas of the individual and it can help them realize their hidden potential.
Psychometric Assessment Using Technology
Personality tests or psychometric tests can be designed, conducted, and managed using technology. Thanks to Online Assessment Platforms, you can easily customize and design online tests according to your needs.
You can classify questions based on a particular topic like Team Building, Sales Management, Pre-Sales Management, Technical Support, etc. Questions can also be classified based on topics like cognitive abilities, adaptive behavior, etc.
You can define a test that can help you understand the candidate’s temperament, adaptive behavior, and cognitive abilities.
What is Cognitive Ability?
First, let us try to understand the meaning of the word cognition.
The dictionary meaning of the word cognition is:
The mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses.
The cognitive ability test refers to the ability of the individual to understand the information presented in various formats like discussions, interactions, videos, life, and work experiences, challenges to tackle particular things, learning new things from case studies, experiences of other people, etc.
Can you Test Cognitive Ability?
Cognitive ability tests can help to identify if a particular person has the ability to learn new things and quickly adapt to new processes, new tasks, and new innovations in the organization.
For any organization, innovation and adopting new technologies is the key to continued and lasting growth. When you are recruiting new employees, it would be useful to understand the cognitive ability of the person to know their attention span, and ability to learn new things and quickly implement them.
You can define online tests with gamification to identify the attention span of the individual or the ability of the individual to focus on a particular thing.
Let us consider the following example for cognitive ability- QU&82UiWk
Identify and match the above sequence with one of the below sequences which match it.
- QU&82UWk
- QU&82UiWk
- QU&42UiWk
- QU$82UiWk
The total time assigned for this question can be, say, 3 to 4 seconds. Such a test would evaluate the ability of the individual to recognize a pattern of words shown and the ability to quickly match this pattern with the options provided.
You can easily check the ability of the individual to quickly comprehend the information provided. Many organizations are coming up with cognitive ability tests to know in detail the cognitive ability of the individual, who will learn new things and overall mental capability.
This test helps organizations to select suitable candidates during hiring or promotion activities.
Psychometric test for entrepreneurs
There are tests designed in such a way that they would enable you to assess the entrepreneurship ability of the individual. Entrepreneurship involves multitasking roles and your ability to work in a team, ability to motivate the team, financial management, and perseverance would be tested.
One of the leading multinational companies, Essilor has come up with a unique test that can evaluate the entrepreneurship ability of the individual. Such tests have been used to identify if a person is suitable to run franchise operations at a particular location.
Whenever the company gets a franchise application, the applicant is supposed to appear for an Entrepreneurship Ability Test which helps the organization in making the decision to award a franchise for a particular location or city.

Conclusion
Psychometric tests or personality tests are evolving quickly with the help of technology. Many organizations have reported better decision-making processes and analyses of the individual using scientifically defined online tests to evaluate the personality and problem-solving ability of the individual.
Psychometric tests help organizations to save time in evaluating individual candidates and it is helping to reduce bias during the hiring or interviewing process.
Do you want to design a Psychometric Assessment for your organization?
Eklavvya is an award-winning platform used by hundreds of organizations and universities to conduct assessments and examinations.
You can subscribe to the Eklavvya platform and design your own custom psychometric test to simplify the evaluation and assessment process for your organization.
What do our customers say about us?
We have been using the Eklavvya platform for assessing the Entrepreneurial Propensity of the candidates for enrollment into our flagship Eye Mitra Opticians program.
Our award-winning Eye Mitra Opticians program aims to help address the issue of 55 crore cases of uncorrected refractive error in India by creating a network of optical micro-entrepreneurs in rural India.
They provide primary vision care services through their micro-franchise outlet as well as by conducting community screening events.The biggest challenge we face is getting the right candidate with the required entrepreneurial capacity and business acumen. To overcome this, we have devised a propensity test (kind of a basic psychometric test with no right or wrong answer) to test the fitment of the candidate.
The platform is quite user-friendly and caters to our requirements of candidate registration, multilingual support, image proctoring, report generation, etc. We look forward to continued support from the Eklavvya team. Thanks.”
Milind Jadhav
Head – 2.5 NVG India Business division of Essilor India Pvt. Ltd.
Online psychometric assessments are tests designed to measure an individual’s personality, mental abilities, and opinions that are administered through an online platform. These tests are based on models and theories of human psychology and are commonly used in the hiring process to evaluate candidates.
Online psychometric assessments are typically administered through a secure, web-based platform. Candidates will be given instructions on how to access the assessment and will be required to log in to complete the test.
Online psychometric assessments can measure a wide range of characteristics, including personality, cognitive abilities, and attitudes. Specific tests may focus on specific areas, such as problem-solving skills or leadership potential.
Online psychometric assessments are generally considered to be reliable measures of an individual’s characteristics. However, it is important to note that no assessment is perfect and it is always important to consider multiple sources of information when making decisions.
Like any test, online psychometric assessments can be subject to bias. It is important to carefully consider the design and administration of the assessment to minimize the potential for bias. In addition, it is important to ensure that candidates have access to the necessary technology and internet connection to complete the assessment.




![How Government-Led Exams at 250+ Locations Are Setting New Standards of Integrity [Case Study]](https://www.eklavvya.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Enhancing-Exam-Integrity-Government-Certification-in-250-Locations-150x150.webp)
![Transforming Central Govt. Exams Evaluation: How Onscreen Marking is Leading the Charge [Case Study]](https://www.eklavvya.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-Onscreen-Marking-Revolutionized-Central-Govt-Exams-Case-Study-1-150x150.webp)















![How Onscreen Marking Revolutionized Central Govt Exams [Case Study]](https://www.eklavvya.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/How-Onscreen-Marking-Revolutionized-Central-Govt-Exams-Case-Study-1-300x300.webp)

